The target protein is involved in the immune system’s response to bacterial infections. It acts as a co-receptor for another immune receptor, which detects pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria.
The target protein binds to LPS and forms a complex with another immune receptor on immune cells like macrophages and dendritic cells. This complex initiates a signaling cascade that leads to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which are crucial for the immune response. The target protein/another immune receptor complex is essential for recognizing bacterial endotoxins, helping to defend the body against bacterial pathogens.
Furthermore, the interaction between the target protein and another immune receptor is being studied in the context of inflammatory diseases and sepsis, where the target protein is considered a potential therapeutic target for managing excessive inflammation in conditions such as sepsis.
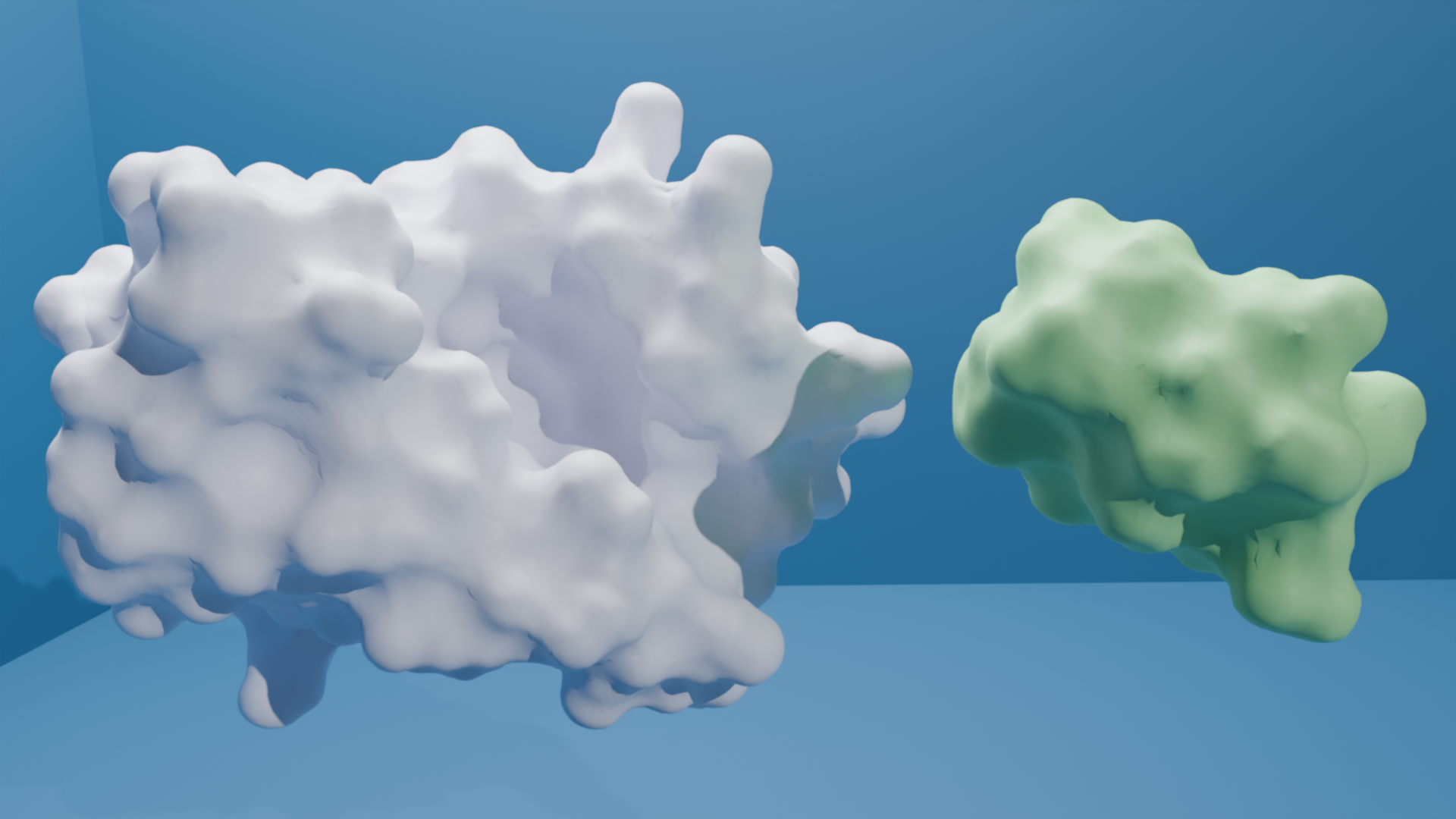
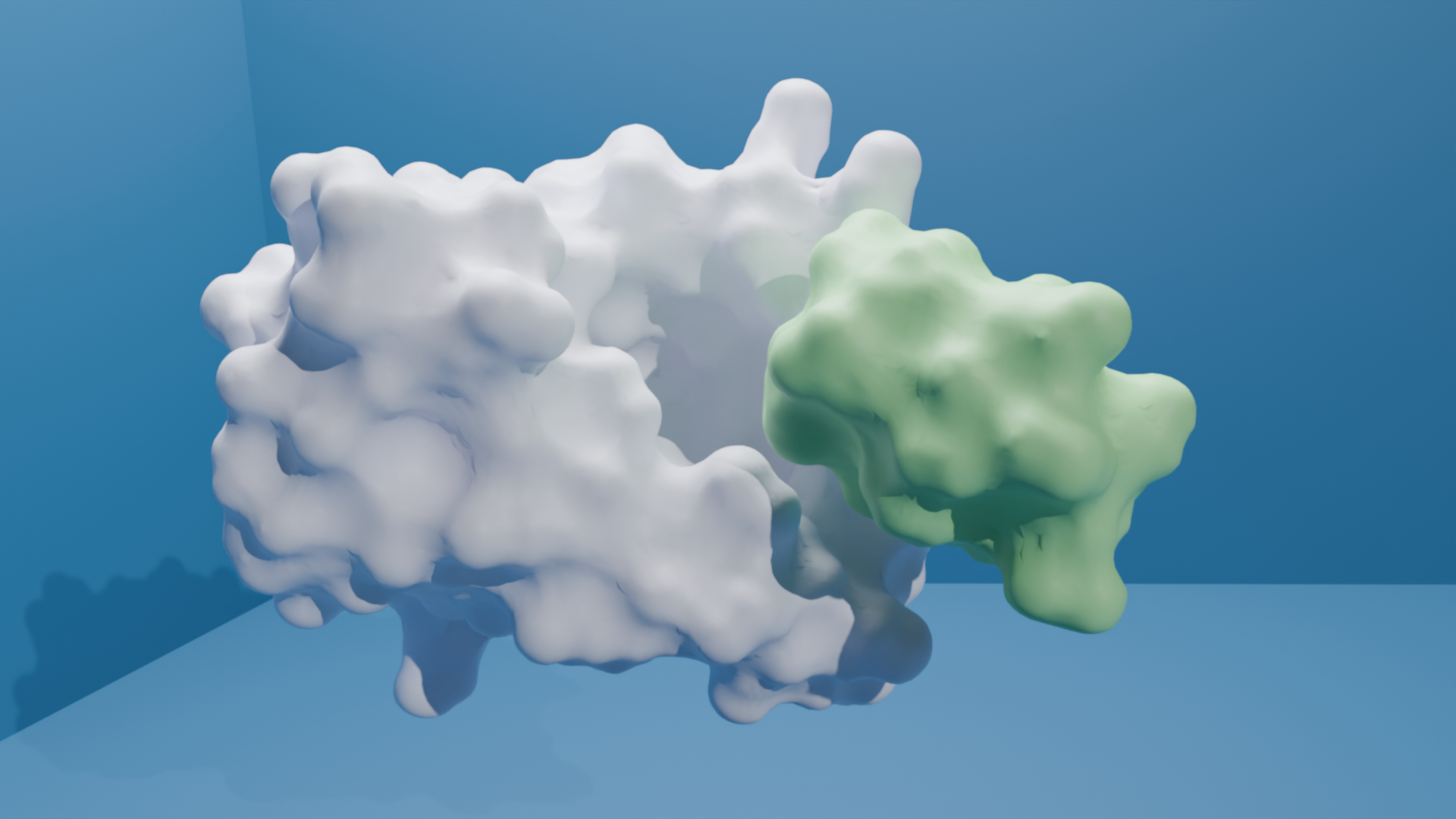
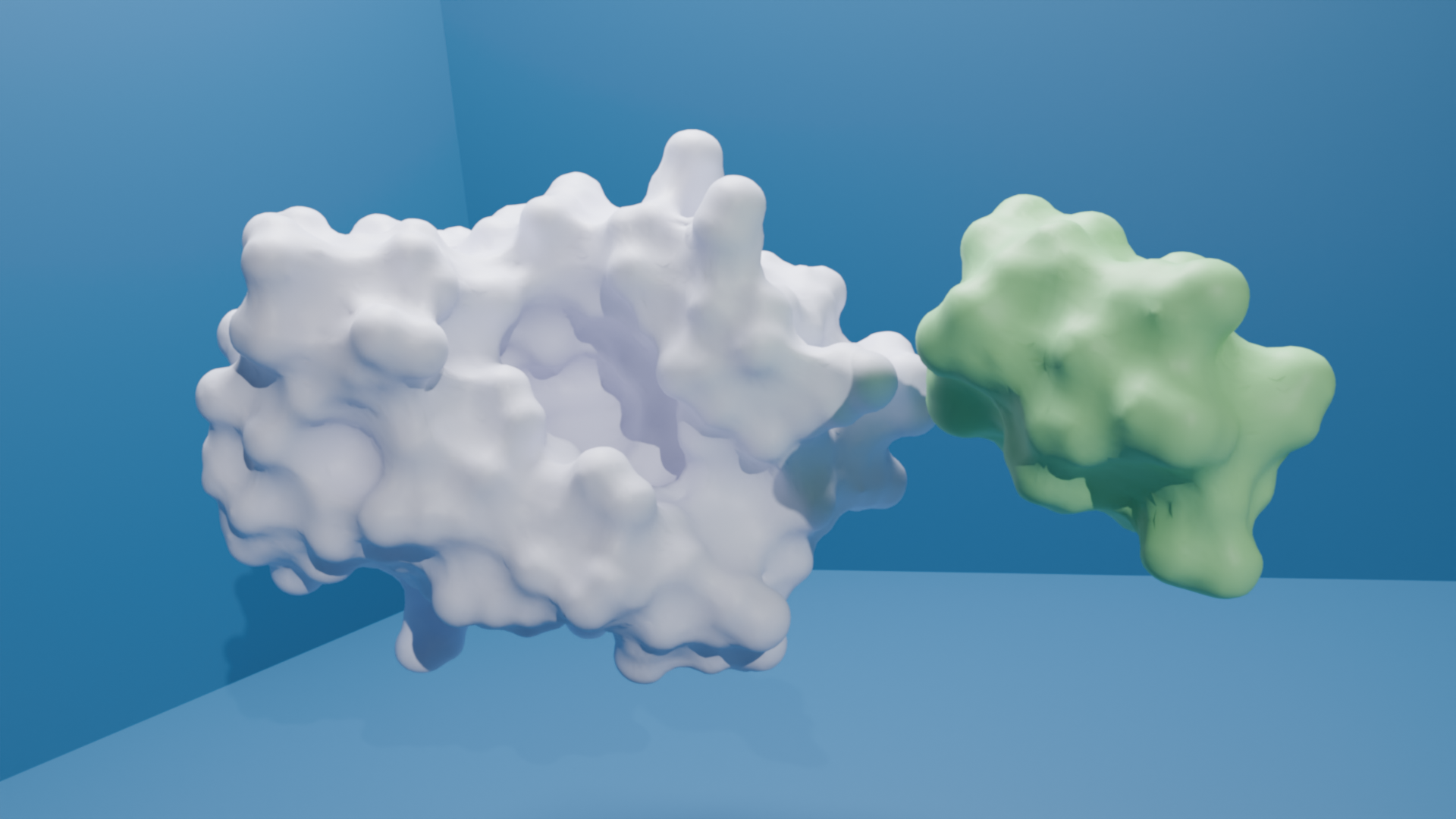
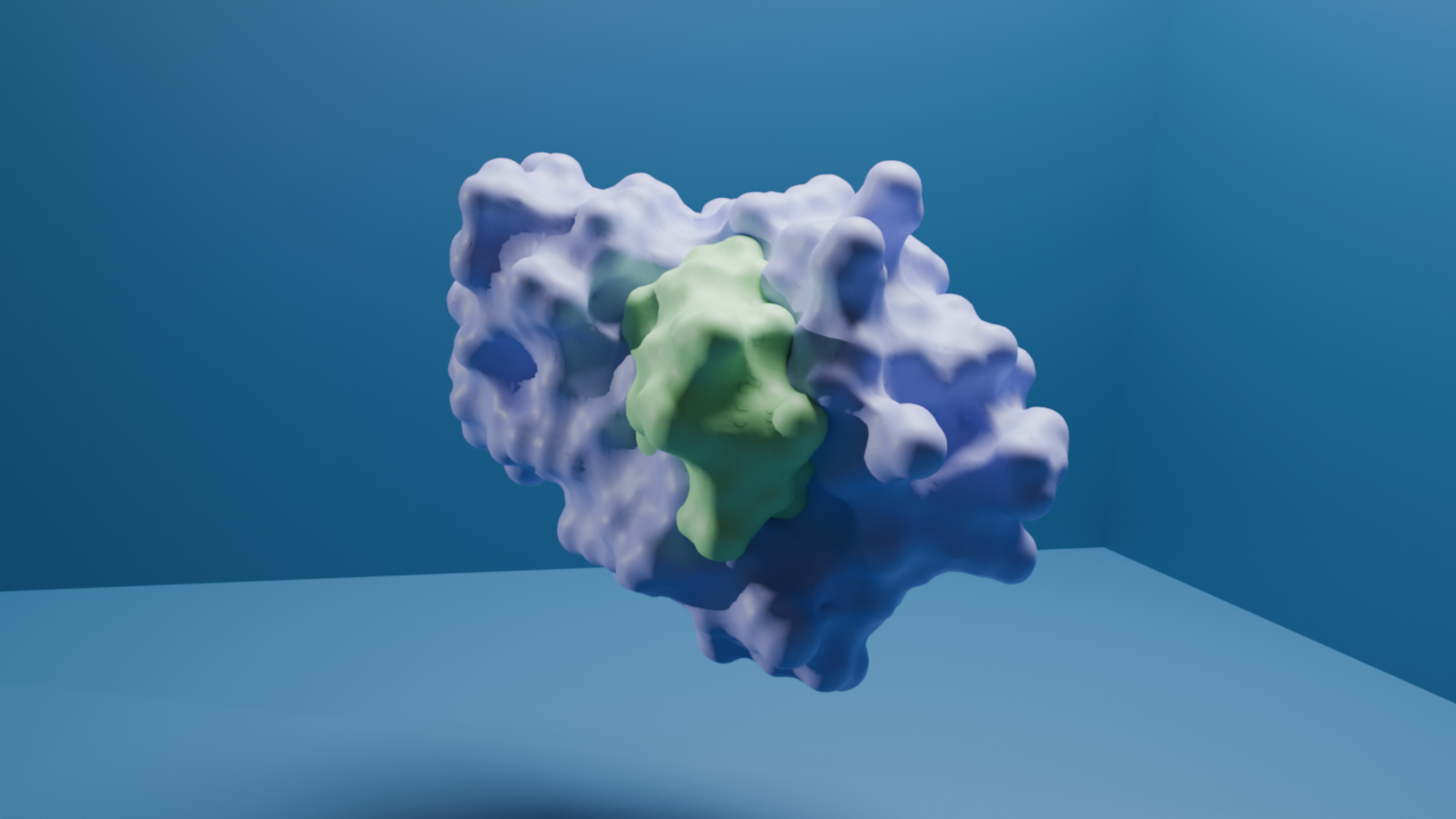
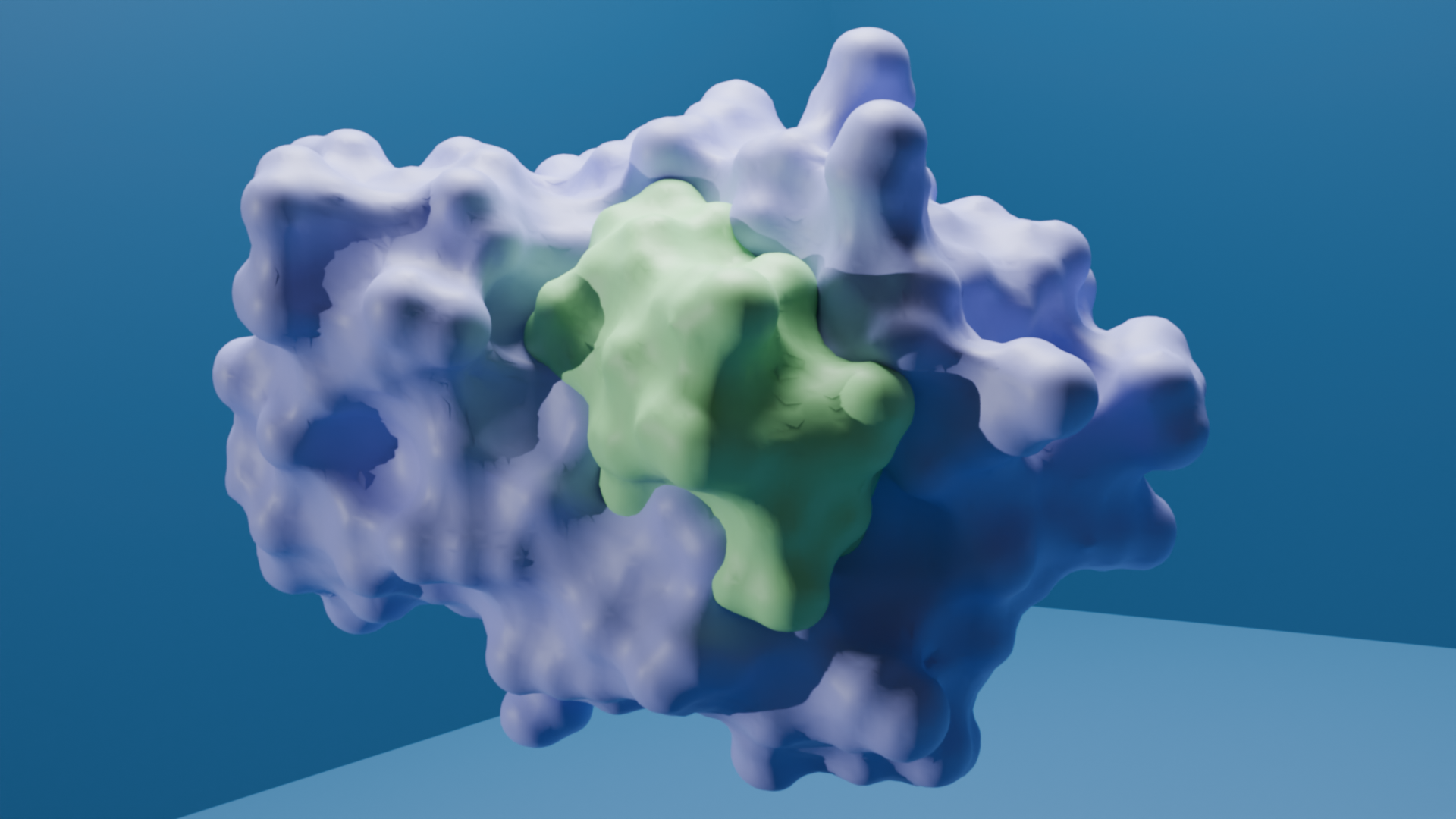
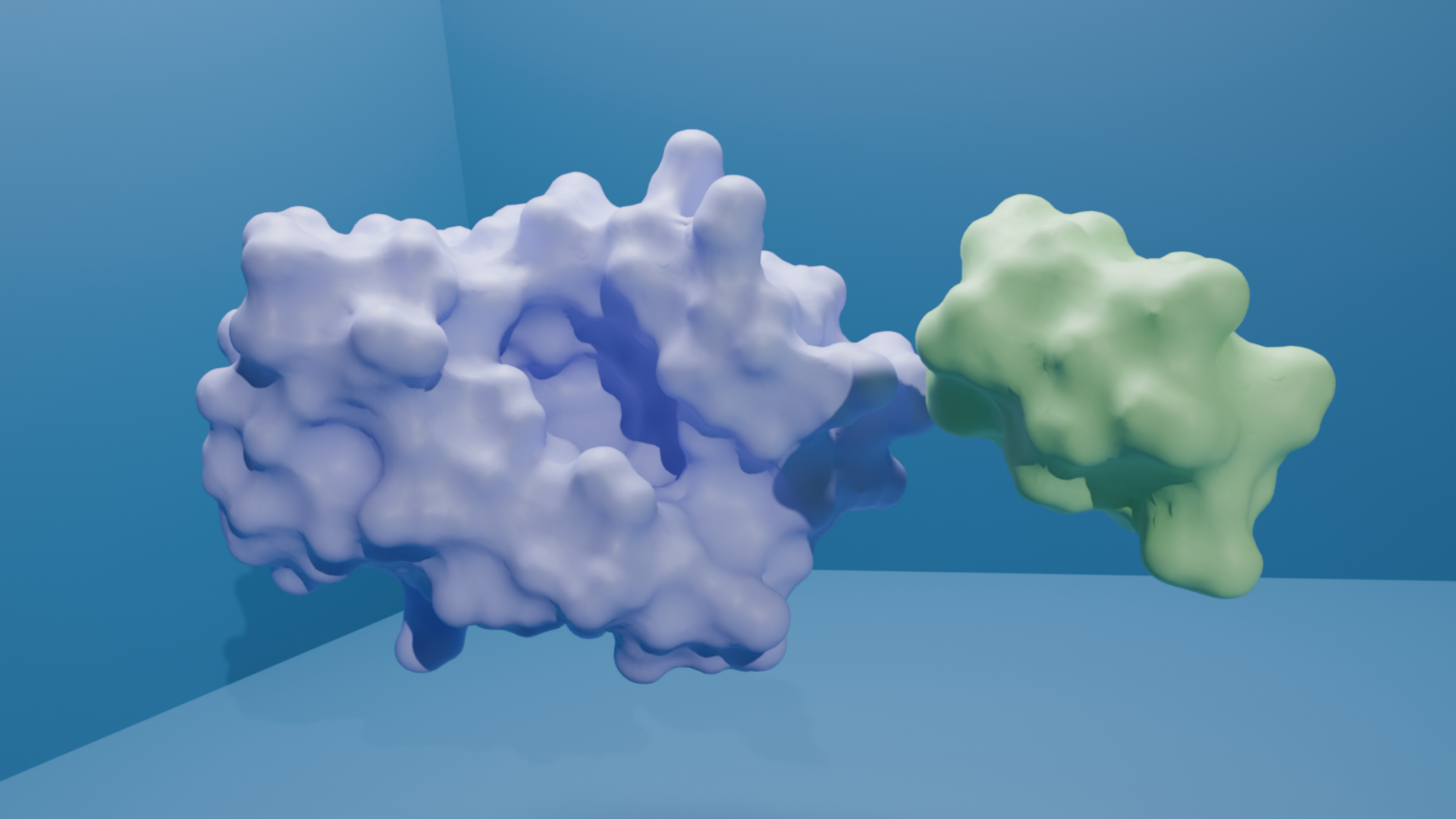
We have designed a molecule, ABS241001, that functions as a minibinder targeting the target protein. ABS24101 binds specifically to the target protein, preventing its interaction with another immune receptor, which is essential for initiating pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. By inhibiting the formation of this complex, ABS241001 disrupts the downstream cascade responsible for producing pro-inflammatory cytokines. This mechanism gives ABS241001 strong potential as an anti-inflammatory agent, offering therapeutic benefits for conditions associated with excessive immune responses, such as sepsis.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.